Otolaryngology - Ear Nose and Throat Disorders
Ava Westwood
Narrator Victoria Andersen
Publisher: Jayjay Ham LLC
Summary
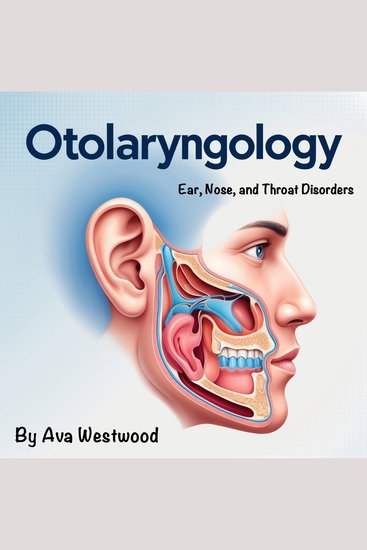
The ear, nose, and throat (ENT) are interconnected structures that perform essential functions such as hearing, balance, respiration, and vocalization. Their anatomical complexity allows them to work together efficiently, contributing to overall health and communication. The ear is divided into three main sections: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The outer ear consists of the auricle (pinna) and the external auditory canal, which collect and direct sound waves toward the tympanic membrane (eardrum). The middle ear houses the ossicles—the malleus, incus, and stapes—which amplify sound vibrations and transmit them to the inner ear. The inner ear contains the cochlea, a spiral-shaped structure that converts sound waves into electrical impulses sent to the brain via the auditory nerve. The inner ear also includes the vestibular system, which regulates balance through the semicircular canals and otolithic organs that detect head movements and spatial orientation. The nose serves both respiratory and olfactory functions. It is structurally divided into the external nose and the internal nasal cavity. The external nose consists of bone and cartilage, while the nasal cavity is lined with mucosa and separated by the nasal septum. Inside the nasal cavity, the nasal conchae (turbinates) filter, warm, and humidify incoming air. The olfactory epithelium, located in the upper nasal cavity, contains specialized receptors that detect odors and transmit sensory information to the brain through the olfactory nerve. Additionally, the paranasal sinuses—frontal, maxillary, ethmoid, and sphenoid—contribute to voice resonance, mucus production, and the reduction of skull weight.
Duration: about 3 hours (02:36:37) Publishing date: 2025-02-26; Unabridged; Copyright Year: — Copyright Statment: —